geekos project 3
项目设计目的
研究进程调度算法,掌握用信号量实现进程间同步的方法。为GeekOS扩充进程调度算法——基于时间片轮转的进程多级反馈调度算法,并能用信号量实现进程协作。
项目设计要求
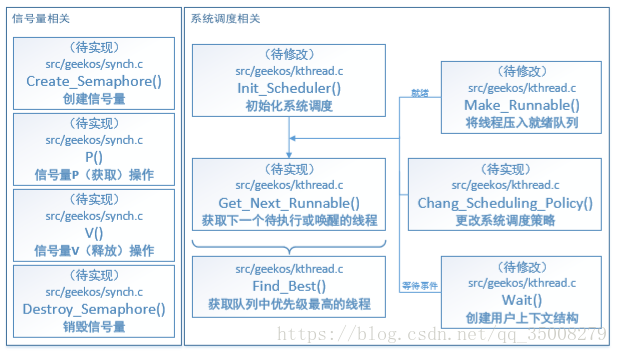
- 实现src/geekos/syscall.c文件中的Sys_SetSchedulingPolicy系统调用,它的功能是设置系统采用的何种进程调度策略;
- 实现geekos/syscall.c文件中的Sys_GetTimeOfDaysrc/系统调用,它的功能是获取全局变量g_numTicks的值;
- 实现函数Change_Scheduling_Policy(),具体实现不同调度算法的转换。
- 实现syscall.c中信号量有关的四个系统调用:sys_createsemaphore( )、sys_P( )、sys_V( )和sys_destroysemaphore( )。
前三个要求都是关于多级反馈调度策略的,第一个是设置,第三个是转换,第二个用来评估算法;第四个要求是有关信号量操作。
GeekOS进程管理
内核进程控制块
系统中每个内核进程有且只有一个进程控制块,进程控制块是用于记录进程状态及有关信息的数据结构。GeekOS操作系统中用数据结构Kernel_Thread作为内核进程控制块,对系统中的进程信息、执行情况、控制信息等加以维护,这个结构在include/kthread.h中定义。
struct Kernel_Thread {
ulong_t esp; /* offset 0 */
volatile ulong_t numTicks; /* offset 4 */
int priority;
DEFINE_LINK(Thread_Queue, Kernel_Thread);
void* stackPage;
struct User_Context* userContext;
struct Kernel_Thread* owner;
int refCount;
/* These fields are used to implement the Join() function */
bool alive;
struct Thread_Queue joinQueue;
int exitCode;
/* The kernel thread id; also used as process id */
int pid;
/* Link fields for list of all threads in the system. */
DEFINE_LINK(All_Thread_List, Kernel_Thread);
/* Array of MAX_TLOCAL_KEYS pointers to thread-local data. */
#define MAX_TLOCAL_KEYS 128
const void* tlocalData[MAX_TLOCAL_KEYS];
/*
* The run queue level that the thread should be put on
* when it is restarted.
*/
int currentReadyQueue;
bool blocked;
};
GeekOS系统中最早的内核进程
GeekOS系统最早创建的内核进程有Idle、Peaper和Main3个进程。在系统初始化时,Main函数调用了一系列初始化函数,其中Init_Scheduler函数(\src\geekos\kthread.c)的作用:geekos project 2
- 初始化一个内核进程mainThread,并将该进程作为当前运行进程;
- 创建两个系统进程Idle和Reaper;
- Idle进程类似于Windows中的系统闲置进程,什么也不做,创建后就一直存在于系统中,它存在的唯一目的是保证准备运行队列中有可调度的进程。当系统没有可运行的进程时,CPU就运行Idle,一旦有其他准备运行的进程进入,Idle就会立即放弃CPU。
- Reaper负责消亡进程的善后工作,如释放消亡进程占用的资源,内存、堆栈等。
void Init_Scheduler(void)
{
g_preSchedulingPolicy = ROUND_ROBIN;
g_curSchedulingPolicy = MULTILEVEL_FEEDBACK;
struct Kernel_Thread* mainThread = (struct Kernel_Thread *) KERN_THREAD_OBJ;
/*
* Create initial kernel thread context object and stack,
* and make them current.
*/
Init_Thread(mainThread, (void *) KERN_STACK, PRIORITY_NORMAL, true);
g_currentThread = mainThread;
Add_To_Back_Of_All_Thread_List(&s_allThreadList, mainThread);
/*
* Create the idle thread.
*/
/*Print("starting idle thread\n");*/
Start_Kernel_Thread(Idle, 0, PRIORITY_IDLE, true);
/*
* Create the reaper thread.
*/
/*Print("starting reaper thread\n");*/
Start_Kernel_Thread(Reaper, 0, PRIORITY_NORMAL, true);
}
内核进程对象
创建一个GeekOS内核进程需要调用Start_Kernel_Thread函数,而Start_Kernel_Thread内部调用Creat_Thread函数 ,该函数主要是创建内核进程对象,并调用Alloc_Page函数为进程对象、进程内核堆栈各分配一页内存(若失败,返回0,同时释放内核控制块空间)。
struct Kernel_Thread* Start_Kernel_Thread(
Thread_Start_Func startFunc,
ulong_t arg,
int priority,
bool detached
)
{
struct Kernel_Thread* kthread = Create_Thread(priority, detached);
if (kthread != 0) {
/*
* Create the initial context for the thread to make
* it schedulable.
*/
Setup_Kernel_Thread(kthread, startFunc, arg);
/* Atomically put the thread on the run queue. */
Make_Runnable_Atomic(kthread);
}
return kthread;
}
进程调度
GeekOS在一下几种情况会发生进程切换:
- 时间片用完;
- 执行内核进程Idle;
- 进程退出调用Exit函数;
- 进程进入等待调用Wait函数。
第一种情况下,当时间片用完,进程切换在中断处理函数Handle_Interrupt(在lowlevel.asm中定义)中完成。
align 8
Handle_Interrupt:
; Save registers (general purpose and segment)
Save_Registers
; Ensure that we're using the kernel data segment
mov ax, KERNEL_DS
mov ds, ax
mov es, ax
; Get the address of the C handler function from the
; table of handler functions.
mov eax, g_interruptTable ; get address of handler table
mov esi, [esp+REG_SKIP] ; get interrupt number
mov ebx, [eax+esi*4] ; get address of handler function
; Call the handler.
; The argument passed is a pointer to an Interrupt_State struct,
; which describes the stack layout for all interrupts.
push esp
call ebx
add esp, 4 ; clear 1 argument
; If preemption is disabled, then the current thread
; keeps running.
cmp [g_preemptionDisabled], dword 0
jne .restore
; See if we need to choose a new thread to run.
cmp [g_needReschedule], dword 0
je .restore
; Put current thread back on the run queue
push dword [g_currentThread]
call Make_Runnable
add esp, 4 ; clear 1 argument
; Save stack pointer in current thread context, and
; clear numTicks field.
mov eax, [g_currentThread]
mov [eax+0], esp ; esp field
mov [eax+4], dword 0 ; numTicks field
; Pick a new thread to run, and switch to its stack
call Get_Next_Runnable
mov [g_currentThread], eax
mov esp, [eax+0] ; esp field
; Clear "need reschedule" flag
mov [g_needReschedule], dword 0
.restore:
; Activate the user context, if necessary.
Activate_User_Context
; Restore registers
Restore_Registers
; Return from the interrupt.
iret
后三种情况,函数内部都有调用Schedule()函数,其中又调用Switch_To_Thread函数(在lowlevel.asm中定义)
align 16
Switch_To_Thread:
; Modify the stack to allow a later return via an iret instruction.
; We start with a stack that looks like this:
;
; thread_ptr
; esp --> return addr
;
; We change it to look like this:
;
; thread_ptr
; eflags
; cs
; esp --> return addr
push eax ; save eax
mov eax, [esp+4] ; get return address
mov [esp-4], eax ; move return addr down 8 bytes from orig loc
add esp, 8 ; move stack ptr up
pushfd ; put eflags where return address was
mov eax, [esp-4] ; restore saved value of eax
push dword KERNEL_CS ; push cs selector
sub esp, 4 ; point stack ptr at return address
; Push fake error code and interrupt number
push dword 0
push dword 0
; Save general purpose registers.
Save_Registers
; Save stack pointer in the thread context struct (at offset 0).
mov eax, [g_currentThread]
mov [eax+0], esp
; Clear numTicks field in thread context, since this
; thread is being suspended.
mov [eax+4], dword 0
; Load the pointer to the new thread context into eax.
; We skip over the Interrupt_State struct on the stack to
; get the parameter.
mov eax, [esp+INTERRUPT_STATE_SIZE]
; Make the new thread current, and switch to its stack.
mov [g_currentThread], eax
mov esp, [eax+0]
; Activate the user context, if necessary.
Activate_User_Context
; Restore general purpose and segment registers, and clear interrupt
; number and error code.
Restore_Registers
; We'll return to the place where the thread was
; executing last.
iret
; Return current contents of eflags register.
以上两个关键函数均在汇编文件中实现,最终执行一个iret指令中断返回,跳入目标进程。
GeekOS进程调度策略
GeekOS的初始系统提供的进程调度是时间片轮转调度,所有准备运行进程(即Kernel_Thread)都放在一个FIFO队列里面,进程调度时找优先级最高的进程投入运行。 在GeekOS中,Get_Next_Runnable函数就是进程调度算法实现的地方,由\src\geekos\kthread.c文件中的Find_Best函数在准备运行进程的队列(s_runQueue指针指向)中查找,找优先级最高的。
项目设计
本项目主要实现多级反馈队列(MLF)和轮询(RR)调度算法以及信号量的相关操作, 需要我们填写 syscall.c 和 kthread.c 等不同文件中的多个函数。 在之前的项目中,GeekOS 使用的系统调度算法均为轮询调度算法,因此在此项目 中,我们需要实现 MLF 调度算法的相关操作以及 RR 与 MLF 两种算法之间的队列转换 算法。GeekOS 中,MLF 算法的规则描述为:进程就绪队列共分为 4 级,按照优先级从 高到低排列分别为 Q0、Q1、Q2 和 Q3 队列;新创建的进程会被置入最高优先级的就绪 队列(此处为 Q0);每当一个进程运行完一个时间片长度之后,它就会被置入比之前低 一级的就绪队列,直到到达优先级最低的队列(Q3), 因此,CPU 密集型的进程最终会 被放到最低优先级的队列中;如果一个进程被阻塞(blocked),它的队列优先级就会提升一个等级,直到被阻塞三次后达到最高优先级队列(Q0)。
在 MLF 策略与 RR 策略的进程队列转换时,GeekOS 给出的规则如下:MLF->RR 时,将 Q1-Q3 队列中所有进程转移至 Q0 队列,然后按照优先级从高到低的顺序重新排 序;RR->MLF 时,只需将原本位于 Q0 队列中的 Idle(空闲)进程转移至 Q3 队列,其 他进程无需再做修改。在实际编写代码的时候,由于 GeekOS 提前实现了从队列中获取 最高优先级进程的函数 Find_Best(),因此在 MLF->RR 时只需要将所有队列中进程移至 Q0 队列中即可。
为实现四级队列,设计中首先要修改s_runQueue(src/geekos/kthreas.c)的定义,从原来一个结构体改为一个4元素的结构体数组,每一个结构体元素用于存放一个优先级队列的队首指针。
GeekOS系统将Idle进程始终放在优先级为3的进程队列末尾,且不允许移动到其它队列,以保证进程调度时一定能找到进程投入运行。
当实现四级反馈队列调度策略后,GeekOS系统就拥有2种进程调度策略,即单队列时间片轮转调度策略和四级反馈队列调度策略。到底采用哪种,是通过系统调用Sys_SetSchedulingPolicy(src/geekos/syscall.c)实现的,函数原型:
static int Sys_SetSchedulingPolicy(struct Interrupt_State* state);
参数state是一个结构体,其中,state->ebx成员用于指定调度策略,值为0代表系统采用时间片轮转调度策略,值为1则代表系统采用四级反馈队列调度策略,若取其他值则出错。state->ecx成员用于记录相应调度策略下的时间片长度。
多级反馈策略测试运行流程
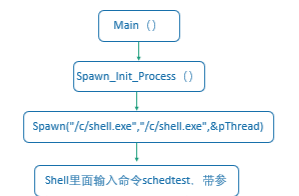
- 补充测试代码
//测试代码
if (argc == 3) {
if (!strcmp(argv[1], "rr")) {
policy = 0;//选择时间片轮转调度
} else if (!strcmp(argv[1], "mlf")) {
policy = 1;//选择多级反馈调度
} else {
Print("usage: %s [rr|mlf] <quantum>\n", argv[0]);
Exit(1);
}
} else {
Print("usage: %s [rr|mlf] <quantum>\n", argv[0]);
Exit(1);
}
quantum = atoi(argv[2]);//设置时间片长度
Set_Scheduling_Policy(policy, quantum);
- 接着调用Sys_SetSchedulingPolicy()(\src\geekos\syscall.c)设置调度策略:
static int Sys_SetSchedulingPolicy(struct Interrupt_State* state)
{
/* 如果输入的优先级调度方法参数无效(非 0 或 1)则返回错误 */
if (state->ebx != ROUND_ROBIN && state->ebx != MULTILEVEL_FEEDBACK)
{
Print("Error! Scheduling Policy should be RR or MLF\n");
return -1;
}
/* 如果输入的时间片参数不在[1, 100]之间则返回错误 */
if (state->ecx < 1 || state->ecx > 100)
{
Print("Error! Quantum should be in the range of [1, 100]\n");
return -1;
}
int res = Chang_Scheduling_Policy(state->ebx, state->ecx);
return res;
}
- 到Chang_Scheduling_Policy()(\src\geekos\kthread.c)修改线程队列及系统相关变量,主要是 g_curSchedulingPolicy 为当前调度策略, g_Quantum 为时间片长度:
int Chang_Scheduling_Policy(int policy, int quantum)
{
/* 如果调度策略不同,则修改线程队列 */
if (policy != g_curSchedulingPolicy)
{
/* MLF -> RR */
if (policy == ROUND_ROBIN)
{
/* 从最后一个线程队列(此处为 Q3)开始将其中的所有线程依次移动到前一个队列,
直到所有线程都移动到 Q0 队列 */
int i;
for (i = MAX_QUEUE_LEVEL - 1; i > 0; i--)
Append_Thread_Queue(&s_runQueue[i - 1], &s_runQueue[i]);
}
/* RR -> MLF */
else
{
/* 判断 Idle(空闲)线程是否在 Q0 队列 */
if (Is_Member_Of_Thread_Queue(&s_runQueue[0], IdleThread))
{
/* 将 Idle 线程从 Q0 队列移出 */
Remove_Thread(&s_runQueue[0], IdleThread);
/* 将 Idle 线程加入到最后一个队列(此处为 Q3) */
Enqueue_Thread(&s_runQueue[MAX_QUEUE_LEVEL - 1], IdleThread);
}
}
/* 保存原来的调度策略 */
g_preSchedulingPolicy = g_curSchedulingPolicy;
/* 将全局变量设置为对应的输入值 */
g_curSchedulingPolicy = policy;
Print("g_schedulingPolicy = %d\n", g_curSchedulingPolicy);
}
g_Quantum = quantum;
Print("g_Quantum = %d\n", g_Quantum);
return 0;
}
- 系统创建进程并运行后,每次时钟中断,进程的numTicks变量加1,这就用到了上面的Time_Interrupt_Handle(/src/geekos/timer.c),通过进程所用时间片与用户输入时间片长度比较,设置g_needReschedule变量,再调用Handle_Interrupt进行进程调度。倘若超过时间片,g_needReschedule为true,Handle_Interrupt就会调用Get_Next_Runnable(\src\geekos\kthread.c),Get_Next_Runnable函数就是进程调度算法实现的地方:
struct Kernel_Thread* Get_Next_Runnable(void)
{
/* Find the best thread from the highest-priority run queue */
KASSERT(g_curSchedulingPolicy == ROUND_ROBIN ||
g_curSchedulingPolicy == MULTILEVEL_FEEDBACK);
/* 查找下一个被调度的线程 */
struct Kernel_Thread* best = NULL;
if (g_curSchedulingPolicy == ROUND_ROBIN)
{
/* 轮询调度策略:只需要从 Q0 队列找优先级最高的线程取出 */
best = Find_Best(&s_runQueue[0]);
/* 如果找到了符合条件的线程则将其从队列中移出 */
if (best != NULL)
Remove_Thread(&s_runQueue[0], best);
}
else
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < MAX_QUEUE_LEVEL; i++)
{
/* 从最高层队列依次向下查找本层队列中最靠近队首的线程,
如果找到则不再向下继续查找 */
best = Get_Front_Of_Thread_Queue(&s_runQueue[i]);
if (best != NULL)
{
Remove_Thread(&s_runQueue[i], best);
break;
}
}
}
/* 如果当前没有可执行进程,则至少应该找到 Idle 线程 */
KASSERT(best != NULL);
return best;
/*
* Print("Scheduling %x\n", best);
*/
}
- 运行结果:
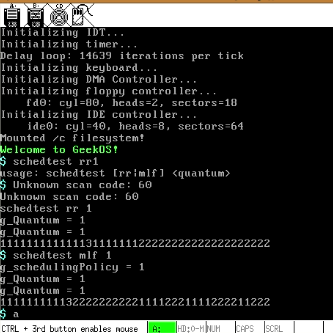
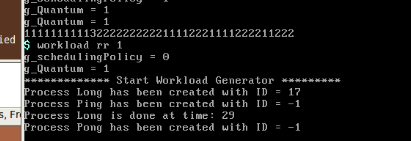
从上面的测试结果来看,这两种调度算法都是基于时间片轮转,输出2和输出1的的数量基本一样多(多队列优先级调度算法的时间片都是一样的)。进程的周转时间还包括进程切换的时间。同样的调度算法,同样的时间片,程序执行的周转时间可能不一样(进程切换花费的时间可能不一样)。
信号量和PV操作
信号量操作: Semaphore_Create( ) Semaphore_Acquire(P操作) Semaphore_Release(V操作) Semaphore_Destroy( )
-
Create_Semaphore()函数首先检查请求创建的这个信号量的名字是否存在,如果存在,那么就把这个线程加入到这个信号量所注册的线程链表上;如果不存在,则分配内存给新的信号量,清空它的线程队列,把当前的这个线程加入到它的线程队列中,设置注册线程数量为1,初始化信号量的名字,值和信号量的ID,并把这个信号量添加到信号量链表上,最后返回信号量的ID。
-
P操作Semaphore_Acquire()中,首先检查传入的信号量ID是否存在,如果存在,接着检查当前线程是否注册使用了这个信号量,如果这两项检查任意一项失败了,那么就返回-1。如果成功了,就把信号量的值减去1,如果减去1后信号量的值小于0,那么就把当前线程放入这个信号量的等待队列上。
-
V操作Semaphore_Release()中,首先也是检查传入的信号量ID是否存在,如果存在,接着检查当前线程是否注册使用了这个信号量,如果这两项检查任意一项失败了,那么就返回-1。如果成功了,那就把信号量的值加上1,如果加上1后信号量的值小于或等于0,则要把该信号量里等待队列上的一个线程唤醒。
-
Semaphore_Destroy()中,首先也是检查传入的信号量ID是否存在,如果存在,接着检查当前线程是否注册使用了这个信号量,如果这两项检查任意一项失败了,那么就返回-1。如果成功了,就把该线程从这个信号量的注册的线程数组中删除,并把注册的线程数量减去1。如果这个信号量的注册线程为0了,则把这个信号量从信号量链表中删除,并释放它的内存。
作业题
- GeekOS 系统原始的线程调度算法是什么?
原始的进程调度是时间片轮转调度
- 在GeekOS 系统中,如何实现多级反馈队列调度算法?
进程就绪队列共分为 4 级,按照优先级从 高到低排列分别为 Q0、Q1、Q2 和 Q3 队列;新创建的进程会被置入最高优先级的就绪 队列(此处为 Q0);每当一个进程运行完一个时间片长度之后,它就会被置入比之前低一级的就绪队列,直到到达优先级最低的队列(Q3), 因此,CPU 密集型的进程最终会被放到最低优先级的队列中;如果一个进程被阻塞(blocked),它的队列优先级就会提升一个等级,直到被阻塞三次后达到最高优先级队列(Q0)。
- 在GeekOS 系统中,如何创建一个信号量?
函数首先检查请求创建的这个信号量的名字是否存在,如果存在,那么就把这个线程加入到这个信号量所注册的线程链表上;如果不存在,则分配内存给新的信号量,清空它的线程队列,把当前的这个线程加入到它的线程队列中,设置注册线程数量为1,初始化信号量的名字,值和信号量的ID,并把这个信号量添加到信号量链表上,最后返回信号量的ID。
- 在GeekOS系统中,如何通过信号量来实现进程同步? PV操作:
P: 首先检查传入的信号量ID是否存在,如果存在,接着检查当前线程是否注册使用了这个信号量,如果这两项检查任意一项失败了,那么就返回-1。如果成功了,就把信号量的值减去1,如果减去1后信号量的值小于0,那么就把当前线程放入这个信号量的等待队列上。
V: 首先也是检查传入的信号量ID是否存在,如果存在,接着检查当前线程是否注册使用了这个信号量,如果这两项检查任意一项失败了,那么就返回-1。如果成功了,那就把信号量的值加上1,如果加上1后信号量的值小于或等于0,则要把该信号量里等待队列上的一个线程唤醒。